






Flux data
Available Data Downloads
Images, Maps, Spectra and SEDs


Infrared data
Radio data
Optical data
X-Ray data




Spitzer IRS spectra

PKS0859-25
Spitzer IRS spectra
Dicken et al. (in preperation)


PKS0859-25
Spitzer MIPS infrared photometric observations. Left to right: 24 microns, 70 microns and 160 microns (when available). FOV are 5x5 arcmins for 24 microns, 5x2.5 arcmins for 70 microns and 0.5x5 arcmins for 160 microns.


![Wavelength/
Frequency Flux Units Reference
5GHz 1.74 Jy Morganti et al. (1993)
[OIII] λ5007 -14.69 Log erg/cm2/s Tadhunter et al. (1993)
15GHz core <1.9 mJy Dicken et al. (2008)
22 GHz core <2.5 mJy Dicken et al. (2008)
24 microns 9.3 mJy Dicken et al. (2008)
70 microns 8.4 mJy Dicken et al. (2008)
160 microns <52.3 mJy Dicken et al. (2008)
X-ray - - -](PKS0859-25_files/shapeimage_19.png)







Other name:
Redshift:
RA (j2000):
Dec (j2000):
Optical class:
Radio Class:

0.305
09 01 47.5
-25 55 19
NLRG
FRII
OJ-299
N

E


Notes
The source PKS 0859−25, which is immersed in a relatively crowded field, appears in our Gemini optical GMOS-S image as a double nucleus system, including the radio galaxy nucleus and a faint component ∼6 kpc the SW (Ramos Almeida et al. 2011a, Fig. B30). This morphological classification is confirmed by the NIR observations and analysis presented by Inskip et al. (2010).
The optical spectrum reveals strong [O III] λλ5007, 4959 and [OII]λ3727 emission lines.


Gemini/GMOS-S: median filtered image
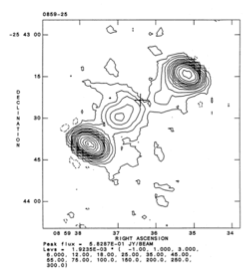
5 GHz VLA radio map
XMM
PKS0859-25
Spectral energy distribution. The blue solid line is fitted to the data from 109 to 1010 Hz. Extrapolating this line from the radio to the infrared SED tests whether non-thermal synchrotron emission from the lobes can contaminate the Spitzer mid-infrared flux. In this case the lobes emission lies out of the Spitzer beam so cannot contaminate the Spitzer data. The weak, flat spectrum, non-thermal radio core emission is also not likely to contaminate the Spitzer infrared flux data for this object.